In today’s fast-paced technology landscape, organizations face numerous IT support challenges like cybersecurity threats, resource limitations, and the constant need to innovate. Many businesses and non-profit organizations grapple with keeping their technology systems running efficiently while ensuring their teams are equipped to meet emerging demands.
This is where co-managed IT support can offer your organization a strategic solution. It empowers your current IT team to leverage external expertise to maximize their internal resources.
Co-managed IT services offer a collaborative approach to technology management. By partnering with an outside resource, companies can enhance their operational capabilities and maintain a competitive edge. Here’s how co-managed IT support can help:
- Enhanced Expertise: Access to a team of seasoned IT professionals with diverse skills and experience.
- Scalability: Flexible support tailored to your organization’s evolving needs, especially during periods of growth or transformation.
- Improved Efficiency: Streamlined IT operations, allowing your internal team to focus on core business strategies.
This guide is designed for a variety of stakeholders, including:
- IT Leaders managing growing teams who need additional support to tackle complex challenges.
- Organizations with existing IT staff seeking enhanced capabilities and specialized knowledge.
- Business Leaders evaluating different IT support models to suit their unique operational needs.
- Companies experiencing rapid growth or embarking on digital transformation initiatives that require robust IT solutions.
- Mid-size businesses striving to balance their internal expertise with the benefits of external support.
Finding a co-managed IT services provider to enhance an organization’s performance and security involves research to find the right partner. We’ve prepared this guide to help navigate the many aspects leaders should consider to identify the right partner.
The Evolution of IT Support Models
The current landscape of IT support has transformed significantly in response to businesses and Non-Profits’ ever-evolving technology demands. Organizations today require comprehensive and adaptive solutions to manage their IT infrastructure effectively. As digital transformation accelerates, the limitations of traditional support models have become increasingly apparent, driving the adoption of more integrated approaches to IT management. Understanding the evolution of these models helps organizations make informed decisions about their IT strategy.
Three Primary IT Support Models
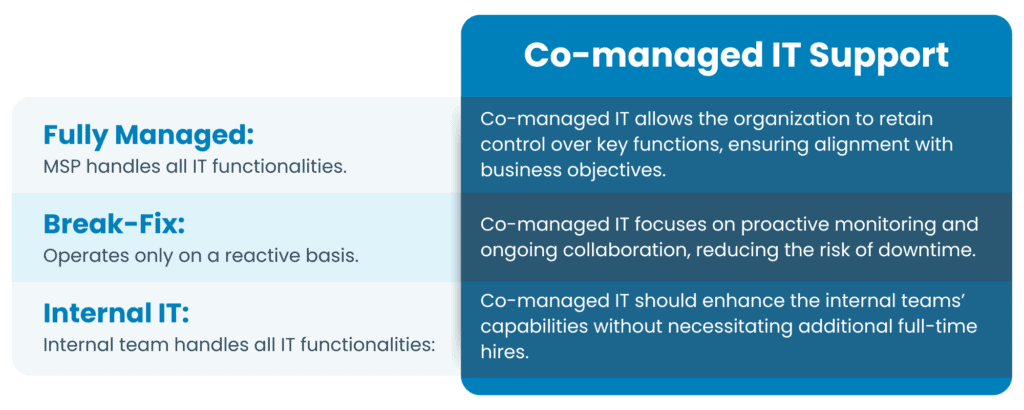
1. Traditional Break-Fix Support: This model operates on a reactive approach, meaning that services are provided only when issues arise.
In this pay-as-you-go model, costs are only incurred when repairs or troubleshooting is required. Support is not proactive so the risk of unscheduled downtime could result in efficiency losses. The lack of preventative measures can also result in frequent disruptions and unexpected costs when problems arise can strain budgets and resources.
2. Fully Managed Services: Fully managed services involve outsourcing all IT support to a third-party provider who handles every aspect of IT management.
Key features of this model include comprehensive coverage of all IT needs, predictable monthly costs, and access to advanced tools and expertise to manage your IT effectively. Organizations with limited budgets could be challenged by the costs associated with fully managed services.
3. Co-Managed IT Services: Co-managed IT services represent a hybrid approach, allowing organizations to retain their in-house IT teams while augmenting them with external expertise.
This increasingly popular service model relies on collaboration between an organization’s internal IT resources and an external support provider. It allows for flexibility in choosing services that enhance existing capabilities, rather than outsourcing everything. As a result, organizations maintain control of their IT strategies but have access to specialized skills and tools as needed for improved efficiency and resilience.
Why Co-Managed IT is Emerging as a Preferred Solution
Co-managed IT services are gaining traction as the preferred IT support model among many organizations because of flexibility, customization, and access to expertise.
- Scalability and Flexibility: As businesses grow, so do their IT needs. Co-managed IT services allow organizations to scale support according to changing needs without overextending their budgets. This flexibility is crucial for businesses undergoing rapid growth or digital transformation.
- Enhanced Security: As cybersecurity threats rise, a co-managed IT solution provides an extra layer of protection by combining internal security protocols with external expertise. This approach ensures a more thorough defense against potential threats.
- Specialized Expertise: Co-managed IT services give businesses access to a wide range of specialized skills and knowledge that may not exist in-house. This can include advanced cybersecurity measures, compliance oversight, and innovative technology solutions tailored to specific needs.
- Efficiency and Focus: By partnering with a co-managed IT provider, internal teams can offload routine tasks and focus on strategic initiatives that drive growth. This increased efficiency often leads to better overall performance and effectiveness in IT operations.
As an organization’s technology needs continue to evolve in the digital age, co-managed IT services are emerging as a viable and efficient solution that balances the best aspects of traditional IT support with the innovation required for future success.
Understanding Co-Managed IT Services
Co-managed Technology services offer organizations a hybrid approach to IT management – blending internal expertise with external support from a Managed Service Provider (MSP). With this model, organizations are more empowered to optimize their IT operations while retaining control over critical processes.
Securing a co-managed IT partnership aims to complement internal IT resources and provide solutions for gaps in expertise, bandwidth, or specific technology needs. Unlike fully outsourced IT services, co-managed IT emphasizes collaboration. The internal IT team retains authority over defined functions, while the MSP provides support tailored to the organization’s needs.
By leveraging the MSP’s tools, expertise, and resources, organizations can enhance efficiency without overburdening their internal staff.
Key Components of a Co-Managed IT Service Model
- Shared Responsibilities: The organization and MSP establish well-defined boundaries for roles and responsibilities often using a Responsibilities Matrix. For instance, the internal team may handle day-to-day support while the MSP manages specialized tasks like cybersecurity or cloud migration.
- Scalable Solutions: Services are typically modular, allowing organizations to scale support up or down based on changing needs, such as growth or new technology rollouts.
- Access to Expertise: MSPs bring deep expertise in areas like cybersecurity, compliance, and network management, filling knowledge gaps within the internal team.
- Advanced Tools and Resources: MSPs provide access to enterprise-grade tools, such as remote monitoring and management (RMM) platforms, which may be cost-prohibitive for smaller organizations to implement independently but are essential for robust cybersecurity and service.
- Proactive Support: Access to continuous monitoring and proactive issue resolution minimizes downtime and ensures IT systems remain operational and secure..
Key Differences between Co-Managed IT and Other Support Models
Customization Options
Organizations can customize a co-managed IT package to address specific needs, such as augmenting support during peak periods or outsourcing niche functions like disaster recovery planning. Some common customizations of support include:
- Cybersecurity: Cybersecurity is a rapidly changing landscape. Taking a partner to help monitor, mitigate, and resolve issues can allow your team to react and protect your environment more efficiently. In addition, co-managed cybersecurity can provide your team with the tools to administer internal training so that your employees are up to date on protecting your organization which is often a benefit when securing cyberliability insurance.
- Help Desk Support and Escalation: Providing your in-house IT support team with a resource to address large technology issues will optimize your organization’s access to the latest and most efficient path to resolution.
- Project Planning and Implementation: Rolling out new technology services and solutions can be challenging for small internal teams. Employing an outside project management resource will help streamline the process and help meet deadlines and budget requirements.
- Technology Strategy and Planning: Partnering with an experienced consultant to plan and budget for future IT needs can reduce surprises while keeping your technology up-to-date.
The most essential component to any co-managed IT partnership is the broad flexibility that it should provide to an internal IT team. They should expect the following from any co-managed IT partnership:
- Adaptability: structured to evolve with the business, accommodating shifts in strategy, technology, or workforce needs.
- Control and Autonomy: organizations maintain control over critical IT decisions while MSPs provide expertise and support, ensuring services align with business goals.
- Cost Efficiency: selectively outsourcing specific functions allows organizations to optimize IT spending and allocate resources strategically.
Co-managed IT services provide a powerful blend of internal control and external expertise, offering flexible and scalable solutions to their IT needs.
Benefits of Co-Managed IT Services
Partnering with a co-managed IT services partner provides numerous advantages, empowering your organization to optimize resources, enhance expertise, and drive growth. Below are the key benefits of co-managed IT services.
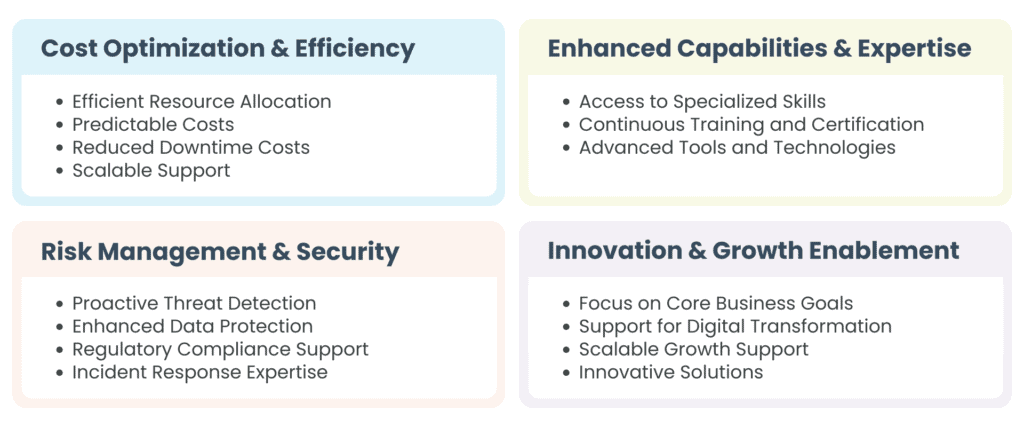
Co-managed IT services empower organizations with cost efficiency, enhanced expertise, robust security, and growth-focused strategies. By partnering with a co-managed IT provider, businesses gain the tools and support necessary to thrive in an increasingly digital and competitive landscape.
Implementation Framework for Co-Managed IT Services
Implementing co-managed IT services involves a structured framework to ensure seamless integration, effective risk management, and measurable outcomes. Below, we outline the key components for incorporating co-managed IT services into everyday business operations.
Assessment and Planning
- Initial Needs Analysis: Evaluate current IT capabilities, including staff expertise, infrastructure, and processes. Identify gaps, such as insufficient bandwidth, lack of specialized skills, or outdated technologies.
- Goal Setting: Define clear objectives for the co-managed IT partnership, such as improving cybersecurity, scaling IT resources, or enhancing operational efficiency.
- Budget Planning: Establish a budget that aligns with organizational goals and ensures cost-effective use of co-managed services.
- Stakeholder Involvement: Engage key stakeholders, including IT leaders, department heads, and the MSP, to ensure alignment of expectations and objectives.
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Develop detailed SLAs that outline the scope of services, response times, escalation procedures, and performance benchmarks.
Integration Strategies and Stand Up
- Collaborative Onboarding: Create a comprehensive onboarding plan that includes knowledge transfer sessions, infrastructure mapping, and tool integration. Establish communication protocols to ensure smooth collaboration between internal teams and the MSP.
- Defined Roles and Responsibilities: Clearly delineate responsibilities to avoid overlaps or gaps. For example:
- Internal IT: Handles day-to-day troubleshooting.
- MSP: Focuses on advanced tasks like network optimization or security monitoring.
- Technology Integration: Implement necessary tools and platforms provided by the MSP, such as Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) systems or ticketing platforms. Ensure compatibility with existing IT systems to avoid disruptions.
- Training and Support: Provide training sessions for internal IT staff to familiarize them with new tools and processes introduced by the MSP. Offer continuous support to address questions or challenges during the transition.
Risk Management Considerations
- Data Security: Assess the MSP’s data protection policies and ensure they align with industry standards. Implement robust encryption, access controls, and backup solutions.
- Compliance Assurance: Verify that the MSP adheres to relevant regulatory requirements (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) to mitigate legal risks.
- Disaster Recovery Plans: Develop a comprehensive disaster recovery plan in collaboration with the MSP to ensure business continuity in the event of cyberattacks or system failures.
- Regular Audits and Reviews: Conduct periodic reviews of the co-managed IT framework to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
Success Metrics and KPIs
- Operational Metrics: Track metrics such as system uptime, mean time to resolution (MTTR), and ticket response times to measure operational efficiency.
- Cost Metrics: Assess cost savings compared to fully outsourced IT or maintaining in-house-only operations. Evaluate ROI based on resource utilization and overall IT performance.
- Security Metrics: Monitor incident response times, threat detection rates, and compliance adherence as indicators of improved security posture.
- Employee Satisfaction: Gather feedback from internal IT staff and end-users to assess the effectiveness and user-friendliness of the co-managed services.
- Scalability and Adaptability: Evaluate how well the co-managed model scales with business growth or adapts to changes in technology or organizational needs.
Successfully onboarding co-managed IT services requires a well-defined framework encompassing thorough assessment, seamless integration, proactive risk management, and measurable success metrics. By following these structured steps, organizations can ensure a successful transition and maximize the value of their co-managed IT partnership.

Core Service Components of a Co-Managed IT Solution
Co-managed IT solutions offer support across key areas of IT operations like help desk, cybersecurity, and infrastructure. These solutions combine internal team efforts with external expertise to provide businesses with a flexible approach to IT management. They empower organizations to enhance everyday workflows while alleviating the burden on internal teams. Below, we outline the core service components of a co-managed IT solution.
Help Desk and Support Services
- 24/7 End-User Support: A dedicated help desk provides round-the-clock assistance, ensuring that employees can resolve technical issues promptly without disrupting productivity.
- Multi-Tiered Support Structure: Includes tiered support levels, from basic troubleshooting (Tier 1) to advanced issue resolution (Tier 3), ensuring that issues are escalated appropriately and efficiently.
- Incident Tracking and Reporting: Comprehensive ticketing systems track incidents, monitor response times, and provide insights into recurring problems to prevent future disruptions.
- Internal Team Collaboration: Co-managed IT teams work seamlessly with internal staff, sharing knowledge and resources to enhance overall support capabilities.
Infrastructure Management
- Network Management: Proactive monitoring of network performance to identify and resolve bottlenecks or outages before they affect operations. Services include configuration, maintenance, and optimization of routers, switches, and access points.
- Server Maintenance: Regular updates, patching, and performance tuning to ensure server reliability and efficiency. This includes support for both on-premises and hybrid server environments.
- Device Management: Lifecycle management of desktops, laptops, and mobile devices, including provisioning, updates, and repairs.
- Scalability and Capacity Planning: Monitoring resource utilization to anticipate and prepare for future growth, such as increasing bandwidth or expanding storage capacity.
Security Operations
- Threat Detection and Response: Continuous monitoring for suspicious activity, leveraging advanced tools like a Security Operations Center (SOC) and systems. For example, detecting and neutralizing phishing attempts or malware attacks in real-time.
- Vulnerability Management: Regular vulnerability scans and penetration testing to identify and address security weaknesses in systems and applications.
- Data Protection and Compliance: Implementation of data encryption, access controls, and multi-factor authentication to secure sensitive information. Assistance with compliance frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS to ensure regulatory adherence.
- Disaster Recovery and Backup: Comprehensive backup solutions with rapid recovery protocols to ensure business continuity in case of data loss or system failures.
Cloud Services Management
- Cloud Strategy Development: Guidance on selecting and implementing cloud solutions that align with business needs, whether public, private, or hybrid environments.
- Cloud Infrastructure Management: Monitoring and maintaining cloud resources, including virtual machines, storage, and applications. For example, your co-managed partner ensures that cloud-hosted applications maintain high availability and performance.
- Cost Optimization: Identifying underutilized cloud resources to optimize spending and eliminate unnecessary costs.
- Migration Services: Assisting with the seamless migration of workloads to the cloud, ensuring minimal downtime and data integrity.
Strategic Technology Planning
- IT Roadmap Development: Creating a long-term strategy for IT growth and modernization, aligned with organizational goals.
- Technology Trends and Insights: Providing access to industry trends and innovations to help organizations stay competitive. One example would be advising on emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, edge computing, or Internet of Things (IoT).
- Budget and Resource Planning: Offering expertise in allocating IT budgets effectively, focusing on high-impact initiatives that drive ROI.
- Performance Analytics: Using analytics to measure the success of IT initiatives and make data-driven decisions for continuous improvement.
The core service components of a co-managed IT solution offer businesses unparalleled support and flexibility, enhancing internal team capabilities and addressing critical IT needs. By providing comprehensive help desk services, robust infrastructure management, advanced security operations, efficient cloud services, and strategic planning, co-managed IT services help organizations optimize their operations and adapt to evolving technological demands. This partnership empowers businesses to focus on growth while ensuring their IT environment is secure, scalable, and future-ready.
Measuring Success
Measuring the success of a co-managed IT solution is essential to ensure that it enhances daily operations and effectively supports internal teams. Key areas to evaluate include:
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- SLA Compliance Rate: Tracks adherence to Service Level Agreements. High compliance reflects reliability and commitment.
- First Contact Resolution Rate: Percentage of issues resolved during the initial contact. Higher rates suggest effective frontline support.
- Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT): Assesses user satisfaction with IT services. Positive scores indicate successful support and service quality.
- System Uptime and Availability: Monitors the operational time of critical systems. High uptime signifies dependable infrastructure management.
- Average Resolution Time: Measures the time taken to resolve IT issues. Shorter times indicate efficient problem-solving and minimal disruption.
Cost vs. Benefit Analysis
A true co-managed services solution is not meant to replace your team but to augment your IT team’s current skill set. A co-managed partner should offer a wide range of services so you can evaluate and use the partnership to fill gaps at a cost-efficient price.
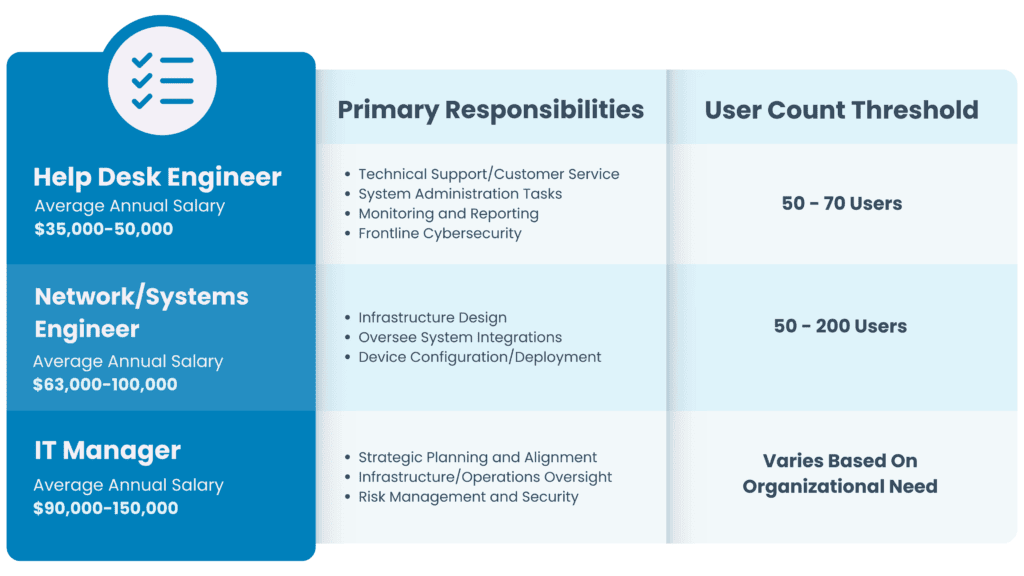
These are a few common IT roles found in small—to medium-sized businesses, but keep in mind that your technology support needs will continue to evolve as your organization grows. Because technology is an essential part of most operations, leadership with expertise will ensure that your IT will support your growth instead of hindering it.
Continuous Improvement Processes
A strong co-managed partner will work with your organization to provide regular performance reviews. They will assess KPIs, identify areas for enhancement, and initiate feedback mechanisms to fully understand your experience.
As your business objectives evolve, you can count on your co-managed services provider to collaborate with you on IT strategy, implement innovative solutions, and ensure both internal and external personnel receive ongoing education to stay current with technological advancements.
By focusing on these metrics and processes, organizations can effectively measure and enhance the success of their co-managed IT solutions, ensuring they provide substantial support to internal teams and contribute positively to daily operations.
Getting Started with a Co-Managed IT Solution
Implementing a co-managed IT solution can enhance your organization’s IT capabilities while relieving the workload of your internal team. Here’s how to get started:
Evaluation Checklist
Before engaging with a co-managed IT provider, assess your current IT environment and needs using these the steps below:
- Identify Pain Points: Are there gaps in expertise, workload bottlenecks, or recurring issues that impede productivity?
- Assess Existing IT Infrastructure: Document the hardware, software, and network systems currently in use.
- Evaluate Internal IT Team Capabilities: Understand your team’s strengths and where external support is needed.
- Set Goals: Define measurable objectives for engaging with a co-managed IT provider, such as improving response times or increasing system uptime.
- Budget Review: Determine your financial constraints and allocate resources for a co-managed partnership.
- Compliance and Security Requirements: Ensure any prospective provider can meet your industry’s regulatory standards.
Next Steps for Implementation
Once you’ve evaluated your needs, it’s time to take steps to begin evaluating potential partnerships. Start by researching providers with experience in your industry and a proven track record of success. Online resources like local periodicals “Best of…” lists or personal referrals from peer groups can be a great place to begin researching.
Once you have identified a list of potential providers, request proposals and demos so you can adequately compare services, pricing, and support models. Be sure to include questions about their transition plan, defining roles and responsibilities and how training will work.
Additional Resources
- Webinars and Case Studies: Explore content from providers to see real-world examples of successful co-managed IT implementations.
- Consult with Experts: Schedule consultations with providers to address specific questions or concerns.
- Technology Assessment Tools: Use online tools or services to evaluate your current IT environment.
By following this structured approach, organizations can confidently transition to a co-managed IT solution that complements their internal capabilities and supports long-term growth.
